Front crash prevention: pedestrian
The pedestrian front crash prevention evaluation represents common daytime and nighttime pedestrian crashes that occur when an adult or child attempts to cross the road or when an adult is walking in the travel lane in same direction as the flow of traffic.
How the test is conducted
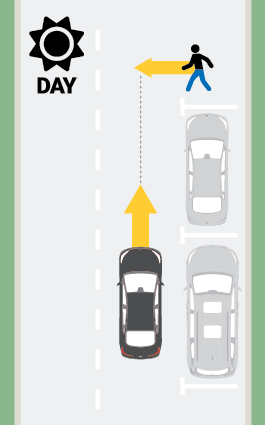
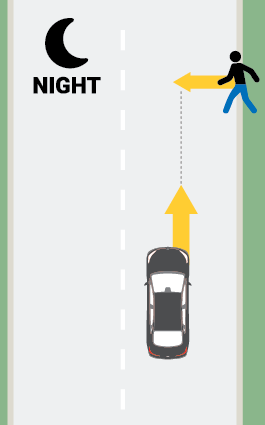
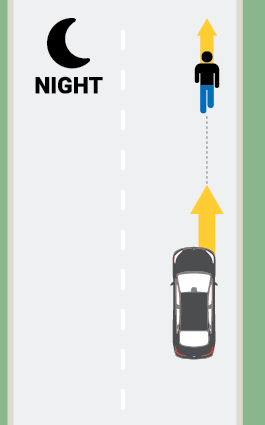
- In the two perpendicular test scenarios, the pedestrian dummy is pulled across the path of the vehicle on a platform as a motor moves its legs to simulate walking. In the parallel scenario, the dummy does not move.
- Test runs involving the adult-size dummy are conducted at night, while the child crossing scenario is conducted in daylight. For vehicles with radar-only systems, all tests may be conducted in the daytime, since such systems are not affected by light levels.
- Prior to 2024, we published separate daytime and nighttime ratings, and the two adult scenarios were conducted both during the day and at night.
- An onboard camera, GPS system and other sensors record any warnings issued by the system and how much the vehicle slows to avoid or mitigate a collision.
- For the nighttime tests, trials are conducted with the headlights on both the low-beam and high-beam settings.
How vehicles are evaluated
- Points are awarded based on the average speed reductions achieved in three test runs conducted at each speed in each test scenario. In the 37 mph parallel adult scenario, vehicles also earn points for forward collision warnings that occur at least 2.1 seconds before the projected time of impact.
- Performance in the two crossing scenarios is weighted more heavily because they represent the most common pedestrian crashes.
- For vehicles equipped with high-beam assist, scoring in the nighttime tests is adjusted to account for the effect of that feature.
Vehicle front crash prevention test protocol and technical information
For details on other tests we conduct, visit the About our tests page.