Small overlap front: driver-side
Rating applies to 2017 models built after January 2017
Tested vehicle: 2017 Tesla Model S 60 4-door
The Tesla Model S was introduced in the 2012 model year. The car is a plug-in battery-electric vehicle with no gasoline or diesel engine to help power the car.
Beginning with 2016 models built after September 2016, the side curtain airbags were lengthened to improve occupant protection in small overlap frontal crashes. Later, beginning with 2017 models built after January 2017, the driver seat belt was modified with the intent of reducing driver forward movement in a frontal crash. (Information about when a specific vehicle was manufactured is on the certification label typically affixed to the car on the driver door or adjacent B-pillar.)
Two tests of the Model S were conducted by the Institute on cars built before and after the driver seat belt modification. Because there were no structural changes, the structure rating is based on the tests of both cars, the first a 2016 model and the second a 2017 model.
The small overlap frontal rating of the Model S applies to the 75 and tested 60 variants, but does not apply to higher-performance variants, including the 100 and since-discontinued 90, which have larger batteries.
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Chest | |
| Hip/thigh | |
| Lower leg/foot | |
|
Driver restraints and dummy kinematics
In the second test, the dummy’s head contacted the frontal airbag but started to move off the left side because the seat belt allowed excessive forward excursion of the head and torso. The side curtain airbag deployed and has sufficient forward coverage to protect the head from contact with side structure and outside objects. The side torso airbag also deployed. Dummy head movement and airbag interaction was similar in the first test. | |
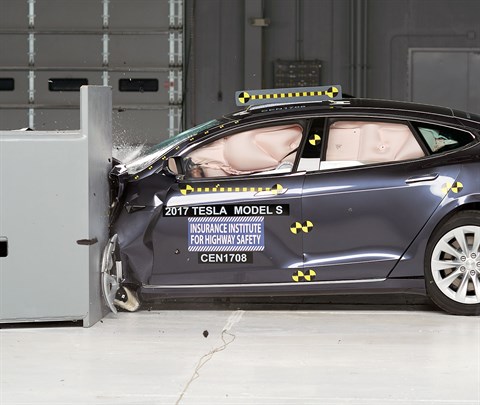

Action shot taken during the second of two small overlap frontal crash tests.
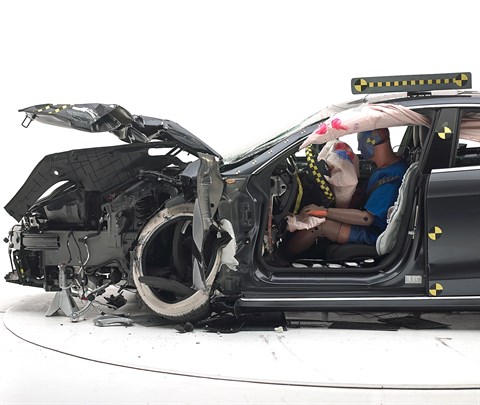

The dummy's position in relation to the door frame, steering wheel, and instrument panel after the second crash test indicates that the driver's survival space was maintained reasonably well overall.
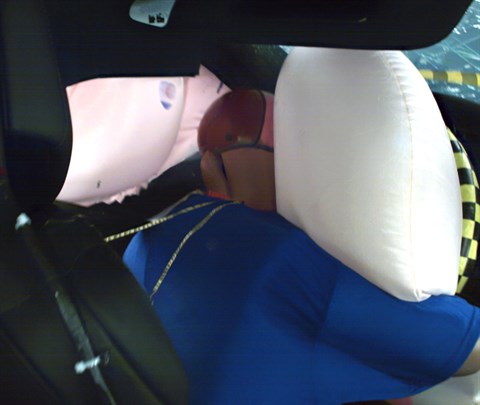

In both tests, the seat belt allowed far too much forward movement of the dummy to the extent that its head hit the steering wheel hard through the airbag (second test shown).
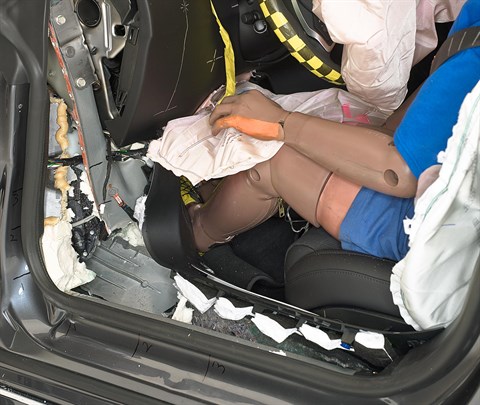

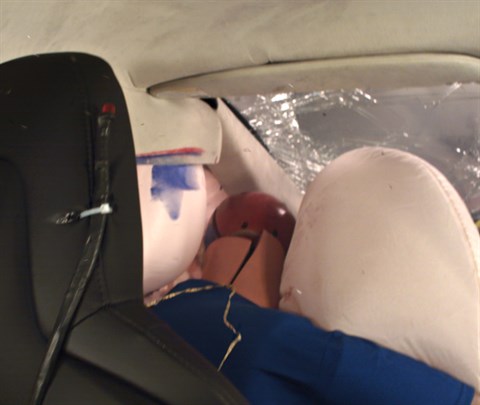
In the second test, the left front wheel was shattered during the crash, but the brake rotor and caliper remained intact and were forced rearward and inward, splitting the welded seam of the door hinge pillar, and contributing to a moderate risk of injury to the left lower leg.
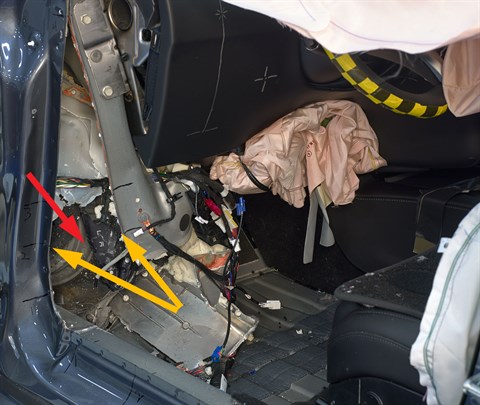

With the carpeting, insulation, and rubber removed, the intruding brake rotor and adjacent caliper (red arrow) and separation between the outer and inner portions of the hinge pillar (yellow arrows) are more readily apparent.
Rating applies to 2016-17 models built after September 2016 and before February 2017
Tested vehicle: 2016 Tesla Model S 60 4-door
The Tesla Model S was introduced in the 2012 model year. The car is a plug-in battery-electric vehicle with no gasoline or diesel engine to help power the car.
Beginning with 2016 models built after September 2016, the side curtain airbags were lengthened to improve occupant protection in small overlap frontal crashes. Later, beginning with 2017 models built after January 2017, the driver seat belt was modified with the intent of reducing driver forward movement in a frontal crash. (Information about when a specific vehicle was manufactured is on the certification label typically affixed to the car on the driver door or adjacent B-pillar.)
Two tests of the Model S were conducted by the Institute on cars built before and after the driver seat belt modification. Because there were no structural changes, the structure rating is based on the tests of both cars, the first a 2016 model and the second a 2017 model.
The small overlap frontal rating of the Model S applies to the 75 and tested 60 variants, but does not apply to higher-performance variants, including the 100 and since-discontinued 90, which have larger batteries.
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Chest | |
| Hip/thigh | |
| Lower leg/foot | |
|
Driver restraints and dummy kinematics
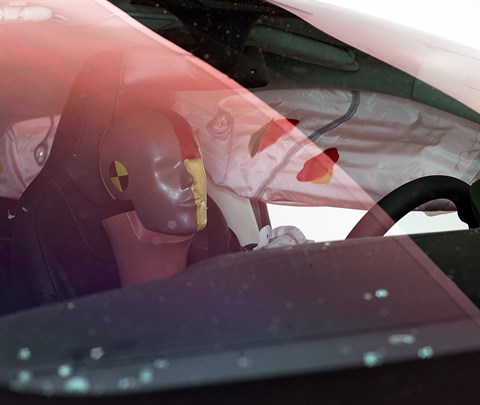
In the first test, the dummy’s head contacted the frontal airbag but started to slide off the left side because the seat belt allowed excessive forward excursion of the head and torso. The side curtain airbag deployed and has sufficient forward coverage to protect the head from contact with side structure and outside objects. The side torso airbag also deployed. Dummy head movement and airbag interaction was similar in the second test. | |

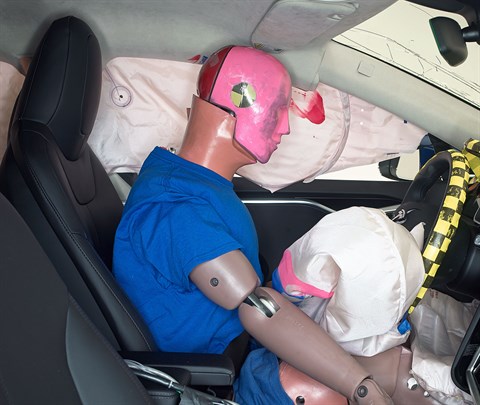
Action shot taken during first of two small overlap frontal crash tests.
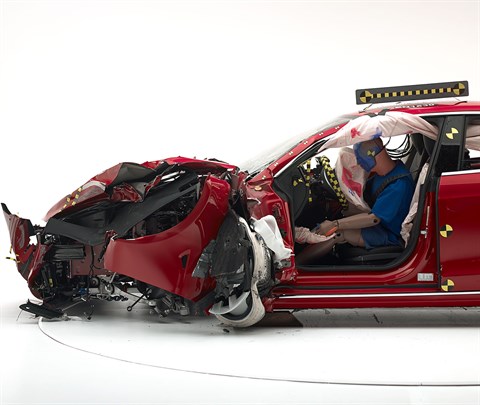

The dummy's position in relation to the door frame, steering wheel, and instrument panel after the first crash test indicates that the driver's survival space was maintained well.
In both tests, the seat belt allowed far too much forward movement of the dummy to the extent that its head hit the steering wheel hard through the airbag (first test shown).
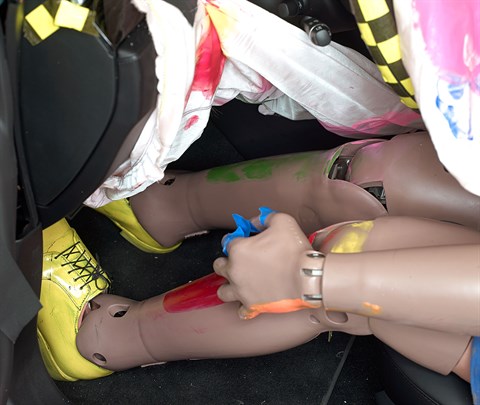

In the first test, forces on the right lower leg were just high enough to indicate a moderate risk of injury (the knee airbag has been pulled upward to make both dummy's legs visible).
Moderate overlap front: original test
Rating applies to 2016-17 models built after October 2016
Tested vehicle: 2016 Tesla Model S 60 4-door
The Tesla Model S was introduced in the 2012 model year. The car is a plug-in battery-electric vehicle with no gasoline or diesel engine to help power the car.
Beginning with 2016 models built after October 2016, a structural brace between the frame and rocker panel was reinforced and deployment guides were added to the side curtain airbags to improve occupant protection in moderate overlap frontal crashes. (Information about when a specific vehicle was manufactured is on the certification label typically affixed to the car on the driver door or adjacent B-pillar.)
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Overall evaluation | |
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Chest | |
| Leg/foot, left | |
| Leg/foot, right | |
| Driver restraints and dummy kinematics | |

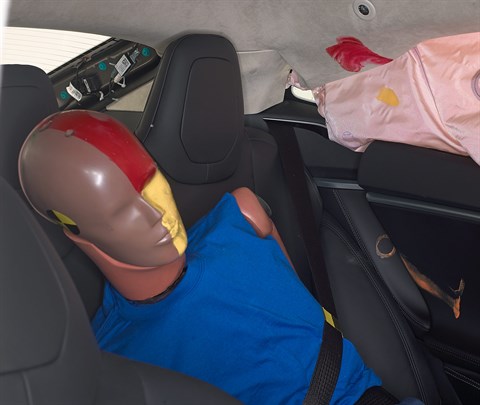
Action shot taken during the moderate overlap frontal crash test.

The dummy's position in relation to the steering wheel and instrument panel after the crash test indicates that the driver's survival space was maintained very well.
Smeared greasepaint indicates where the dummy's head contacted the side curtain airbag during rebound.
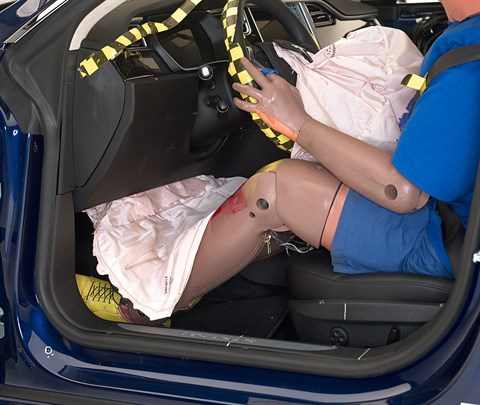
Intrusion into the driver's space was minimal, and all leg and foot injury measures were low.
Side: original test
Rating applies to 2016-17 models built after October 2016
Tested vehicle: 2016 Tesla Model S 60 4-door
The Tesla Model S was introduced in the 2012 model year. The car is a plug-in battery-electric vehicle with no gasoline or diesel engine to help power the car.
Beginning with 2016 models built after October 2016, the B-pillars and roof rails were reinforced and deployment guides were added to the side curtain airbags to improve occupant protection in side impact crashes. (Information about when a specific vehicle was manufactured is on the certification label typically affixed to the car on the driver door or adjacent B-pillar.)
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Overall evaluation | |
| Structure and safety cage | |
| Driver injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Torso | |
| Pelvis/leg | |
| Driver head protection | |
| Rear passenger injury measures | |
| Head/neck | |
| Torso | |
| Pelvis/leg | |
| Rear passenger head protection | |

View of the vehicle and barrier just after the crash test.

View of the vehicle after the crash with doors removed, showing the side airbags and damage to the occupant compartment.

Smeared greasepaint shows where the driver dummy's head was protected from being hit by hard structures by the side curtain airbag.

Smeared greasepaint shows where the rear passenger dummy’s head was protected by the side airbag.
Roof strength
Rating applies to 2016-18 models built after October 2016
Tested vehicle: 2016 Tesla Model S 60 4-door
Rating does not apply to Model S P100D. Rating of this model is Acceptable.
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Curb weight | 4,452 lbs |
| Peak force | 19,271 lbs |
| Strength-to-weight ratio | 4.33 |
Head restraints & seats
Seat type: Power leather seat
| Overall evaluation | |
|---|---|
| Dynamic rating | |
| Seat/head restraint geometry |
About the head restraint & seat test
Currently, IIHS tests apply only to front seats.
Headlights
Ratings are given for 2 different headlight variations available on this vehicle.
Trim level(s)
- 60 trim
- 60D trim
- 75 trim
- 75D trim
- 90D trim
- 100D trim
- P100D trim
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Low-beam headlight type | LED reflector |
| High-beam headlight type | LED reflector |
| Curve-adaptive? | No |
| High-beam assist? | Yes |
|
Overall rating | |
| Distance at which headlights provide at least 5 lux illumination: | |
Low beams
On the straightaway, visibility was fair on both sides of the road. On curves, visibility was inadequate in all 4 tests.
The low beams created some glare.
High beams
On the straightaway, visibility was good on both sides of the road. On curves, visibility was inadequate in all 4 tests.
High-beam assist compensates for some limitations of this vehicle's low beams on the straightaway and all 4 curves.
Trim level(s)
- 60 trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
- 60D trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
- 75 trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
- 75D trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
- 90D trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
- 100D trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
- P100D trim equipped with Premium Upgrades package
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Low-beam headlight type | LED reflector |
| High-beam headlight type | LED reflector |
| Curve-adaptive? | Yes |
| High-beam assist? | Yes |
|
Overall rating | |
| Distance at which headlights provide at least 5 lux illumination: | |
Low beams
On the straightaway, visibility was fair on both sides of the road. On curves, visibility was inadequate in all 4 tests.
The low beams created some glare.
High beams
On the straightaway, visibility was good on both sides of the road. On curves, visibility was inadequate in all 4 tests.
High-beam assist compensates for some limitations of this vehicle's low beams on the straightaway and all 4 curves.
Front crash prevention: vehicle-to-vehicle
Child seat anchors
Rating applies to 2016-17 models
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Overall evaluation | |
| Vehicle trim | 60 Base Leather |
| Seat type | leather |
This vehicle has 2 rear seating positions with complete child seat attachment (LATCH) hardware.
It has 1 additional seating position with a tether anchor only.
| Evaluation criteria | Rating |
|---|---|
| Overall evaluation | |
| Vehicle trim | 60 Base Leather |
| Seat type | leather |
| Rating icon | Rating |
|---|---|
| G | Good |
| A | Acceptable |
| M | Marginal |
| P | Poor |
| Seating positions that rely on borrowed lower anchors or have only a tether anchor available are not rated. | |
thether anchor symbol | Tether anchor |
lower anchor symbol | Lower anchors |
| Lower anchor(s) can be borrowed from adjacent positions(s) | |
| No hardware available |
Details by seating position
| Position | Rating |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| Tether anchor | |
| easy-to-find location | |
| no other hardware could be confused for anchor | |
| Lower anchors | |
| too deep in seat | |
| not too much force needed to attach | |
| difficult to maneuver around anchors | |
| 2 | |
| Tether anchor | |
| easy-to-find location | |
| no other hardware could be confused for anchor | |
| Lower anchors | |
| none available | |
| 3 | |
| Tether anchor | |
| easy-to-find location | |
| no other hardware could be confused for anchor | |
| Lower anchors | |
| too deep in seat | |
| not too much force needed to attach | |
| difficult to maneuver around anchors |
